SOLISCADA V7.50.00.02 is now available. Faster graphics rendering, new Web Server controls, improved reporting and more. Learn what's new and update now→

SOLISCADA supports setting dynamic properties for simple graphic objects and controls to realize visual behaviors and animated graphic properties such as move, scaling, fill, rotation, blinking, flow, and color changes.
This article continues to share several commonly used dynamic properties.
Move
Use numerical data to control horizontal or vertical translation of a graphic object.
Horizontal/vertical movement can be configured as relative or absolute:
l Relative movement — movement is performed relative to a specified graphic object.
l Absolute movement — movement occurs within a fixed, configured range.
Positioning mode: choose Relative.
Minimum / Maximum: the data-value range (from the data source) that effectively controls the graphic object’s movement relative to the selected boundary.
Corresponding position: the pixel range over which the graphic object will move (typically the left/right or top/bottom edges of a given graphic object). You may select relative positions by drag-and-drop, or enter expressions such as objectName.right and objectName.left manually.
Example
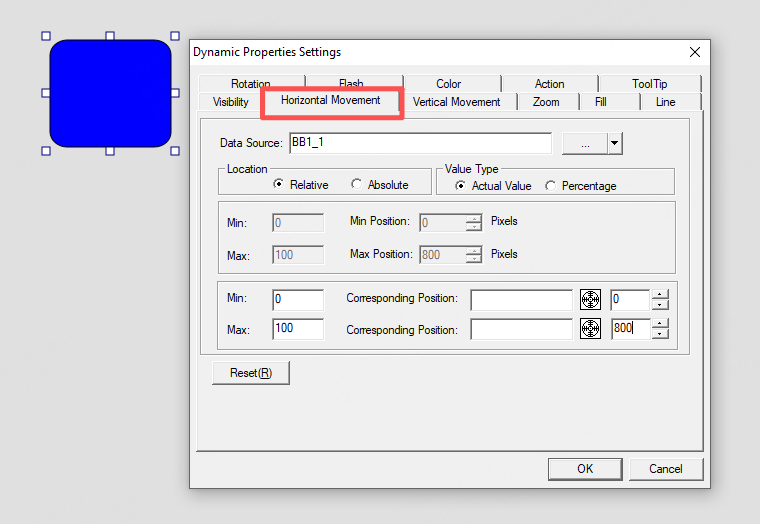
Horizontal movement:
When the tag BB1_1 = 0, the blue graphic is at pixel position 0 (left boundary). When BB1_1 = 100, the blue graphic is at pixel position 1000 (left boundary).
Example
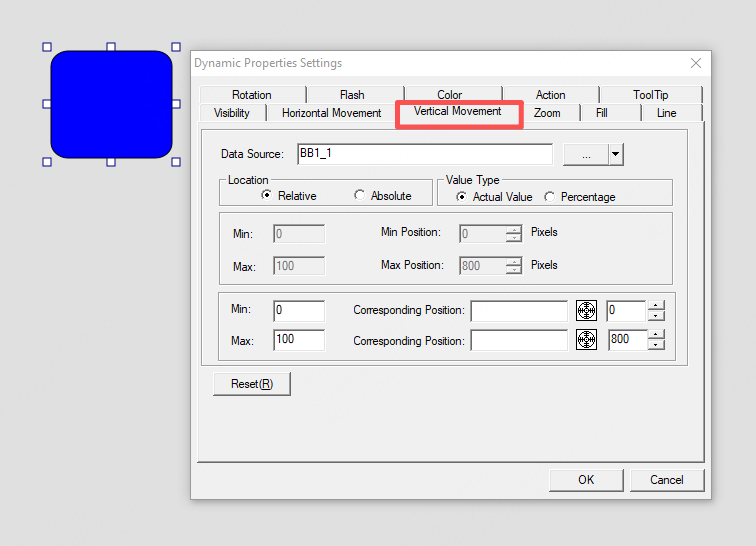
Vertical movement:
When the tag BB1_1 = 0, the blue graphic is at pixel position 0 (top boundary). When BB1_1 = 100, the blue graphic is at pixel position 800 (top boundary).
Flow
To create more realistic animations for piping or conduit graphics, apply the Flow dynamic attribute. Flow is a specialized dynamic attribute for pipe-type graphic objects.
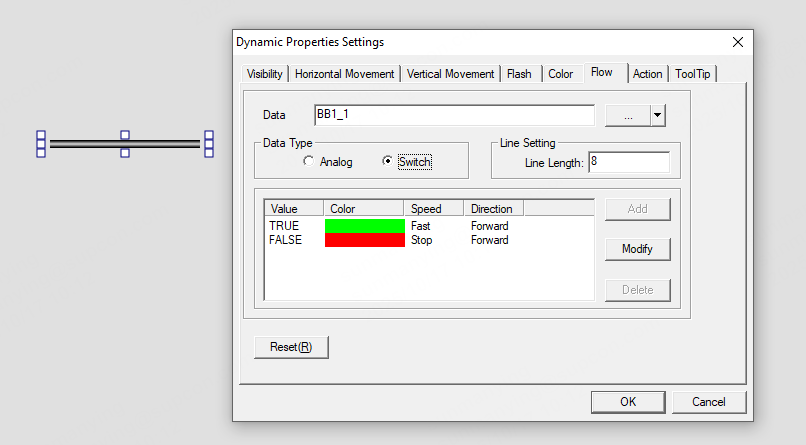
Line length: the length (in pixels) of the flowing “fluid block.” Default = 8; adjust as required.
Parameter settings: click Add and specify the lower/upper limits, choose a color scheme, set flow speed and direction. Repeat to create multi-segment color fills. To edit a row, select it and click Modify (or double-click the row), then change the limits, color, speed and direction in the dialog. To delete a row, select it and click Delete.
Example
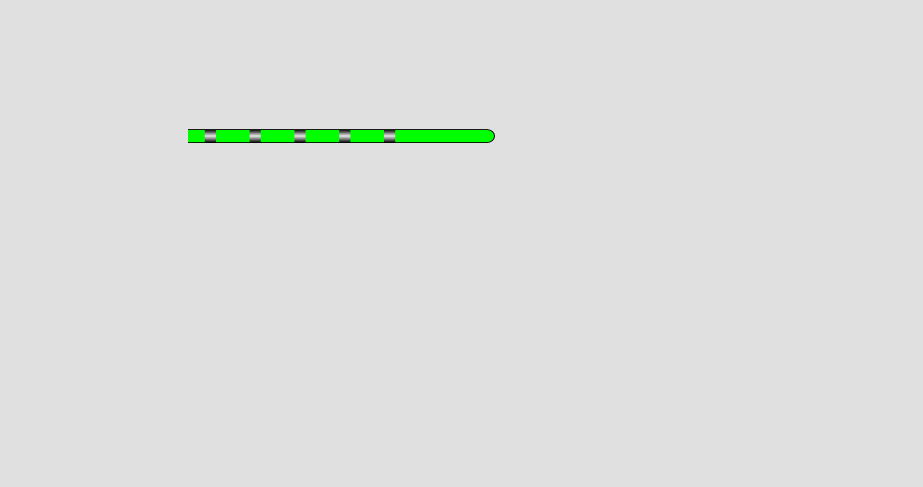
Discrete (digital) input:
When the tag BB1_1 is true, the pipe shows a flowing animation with green internal color. When BB1_1 is false, the pipe shows a flowing animation with red internal color.

Scale
Use numerical data to control an object’s scaling (size) factor.
Parameter settings:
Minimum / Maximum — the numeric range over which the tag controls scaling (do not exceed the data tag’s engineering limits).
Corresponding scale ratio — the resulting scale factor range applied to the object.
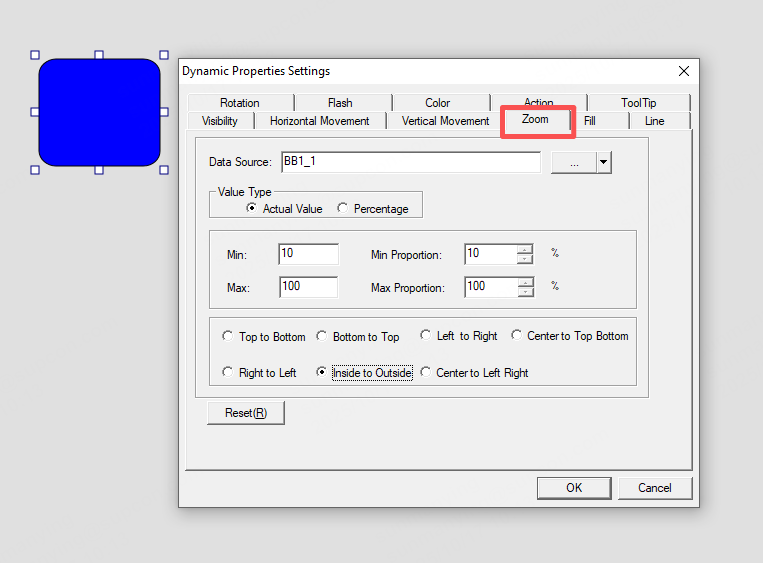
Scaling direction: select one of seven directions:
1. From top to bottom
2. From bottom to topFrom left to right
3. From center toward top and bottom
4. From right to left
5. From inside to outside
6. From center toward left and right
Example
When the tag BB1_1 = 10, the object scales to 10%. When BB1_1 = 100, the object scales to 100%.
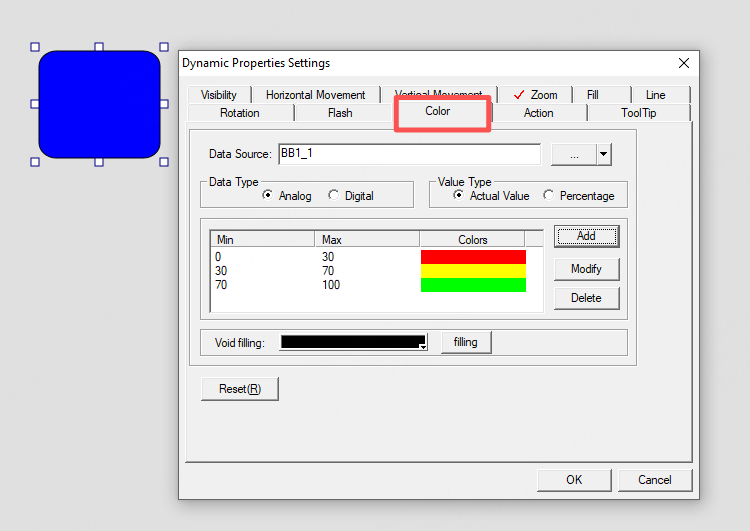
Color
Used to configure a graphic object’s color gradient/change in response to tag value ranges.
Example
l When the tag BB1_1 is in range 0–30, the object color is red.
l When BB1_1 is in range 30–70, the object color is yellow.
l When BB1_1 is in range 70–100, the object color is green.








 Oil & Gas
Oil & Gas Water Industry
Water Industry Food & Pharmaceuticals
Food & Pharmaceuticals Marine
Marine Mining & Metal
Mining & Metal Manufacturing
Manufacturing Electric Utilities
Electric Utilities Municipal Industry
Municipal Industry